Accessing secured Resources
🗓️ Last updated on June 13, 2024 | 3 | Improve this pageOverview
Quickly after your initial experience with Microcks, you’ll realize that it needs to access some of your private resources for smooth integration in your lifecycle. Typically:
- Loading Artifacts may require accessing secured external resources such as Git repositories,
- Launching tests may require accessing protected HTTPS endpoints or internal message brokers.
This guide will explain you what is the concept of Secret in Microcks, how to manage those Secrets and how to use them when defining an Importer Job .
🚨 Prerequisites
Secrets can only be managed by Microcks
admin- we mean people having theadminrole assigned. If you need further information on how to manage users and roles, please check how-to Manage Users .
1. Authentication Secrets
Authentication Secrets (or simply Secrets) are managed by a Microcks administrator and holds credentials for accessing remote resources such as Git repositories, remote API endpoints or event brokers.
Credentials informations wrapped within a Secret can be of several natude like a User/Password pair, a Token or some X509 certificates.
Secrets are stored within the Microcks database and may be reused by regular users when creating an Importer Job or launching a new test. At that time, regular users are just referring Secret name and don’t get access to the detailed.
Secrets management is simply a thumbnail with the Administration page that is available from the vertical menu on the left once logged in as administrator.
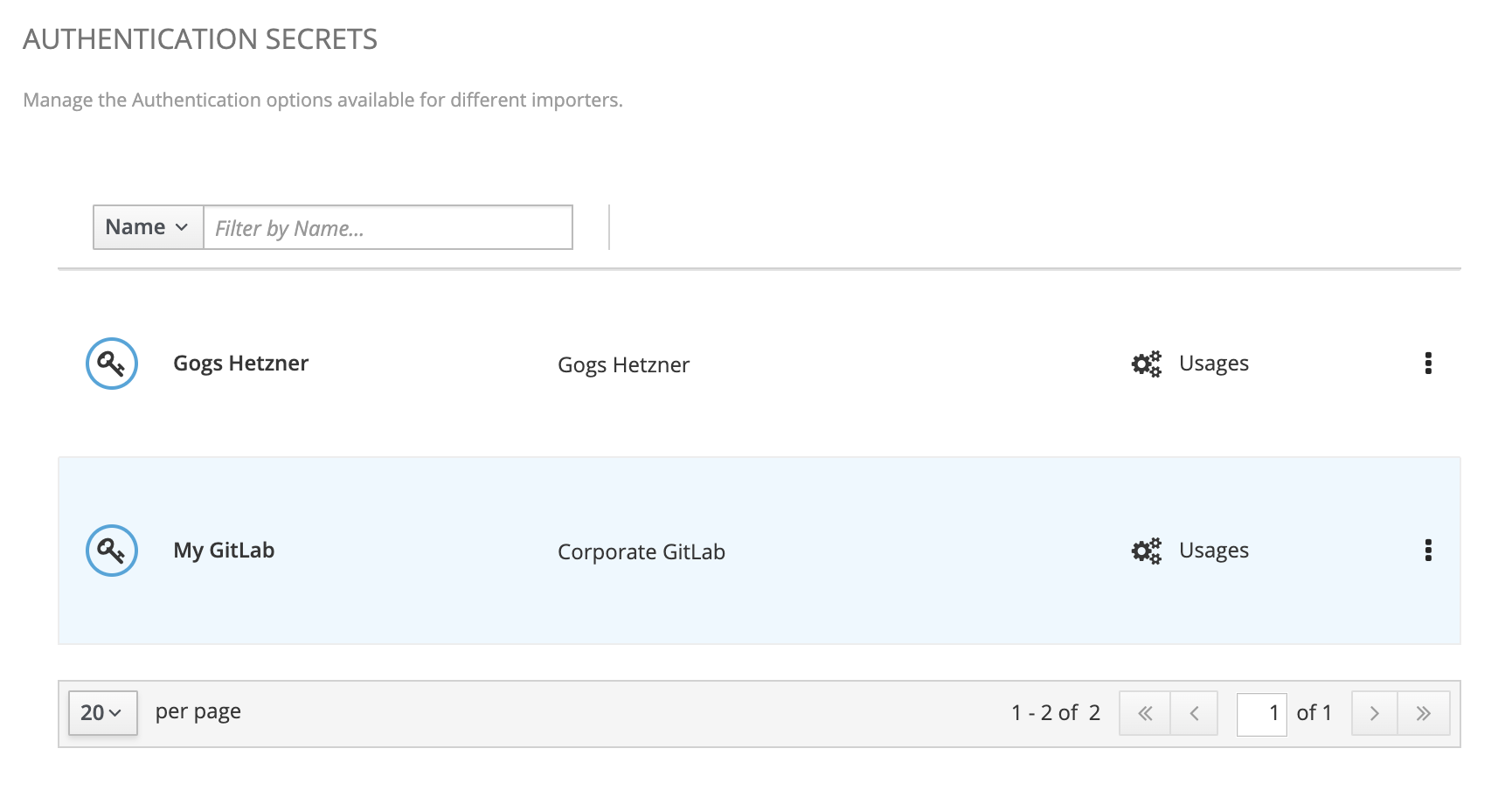
Let see how to create/update a secret and its properties below.
2. Edit Secret properties
Let’s imagine you want to create a secret that will hold informations on how to access your corporate GitLab instance. Here’s the form you’ll have to fill below. It may imply authentication method and properties as well as transport encryption information such as the custom certificate to use.
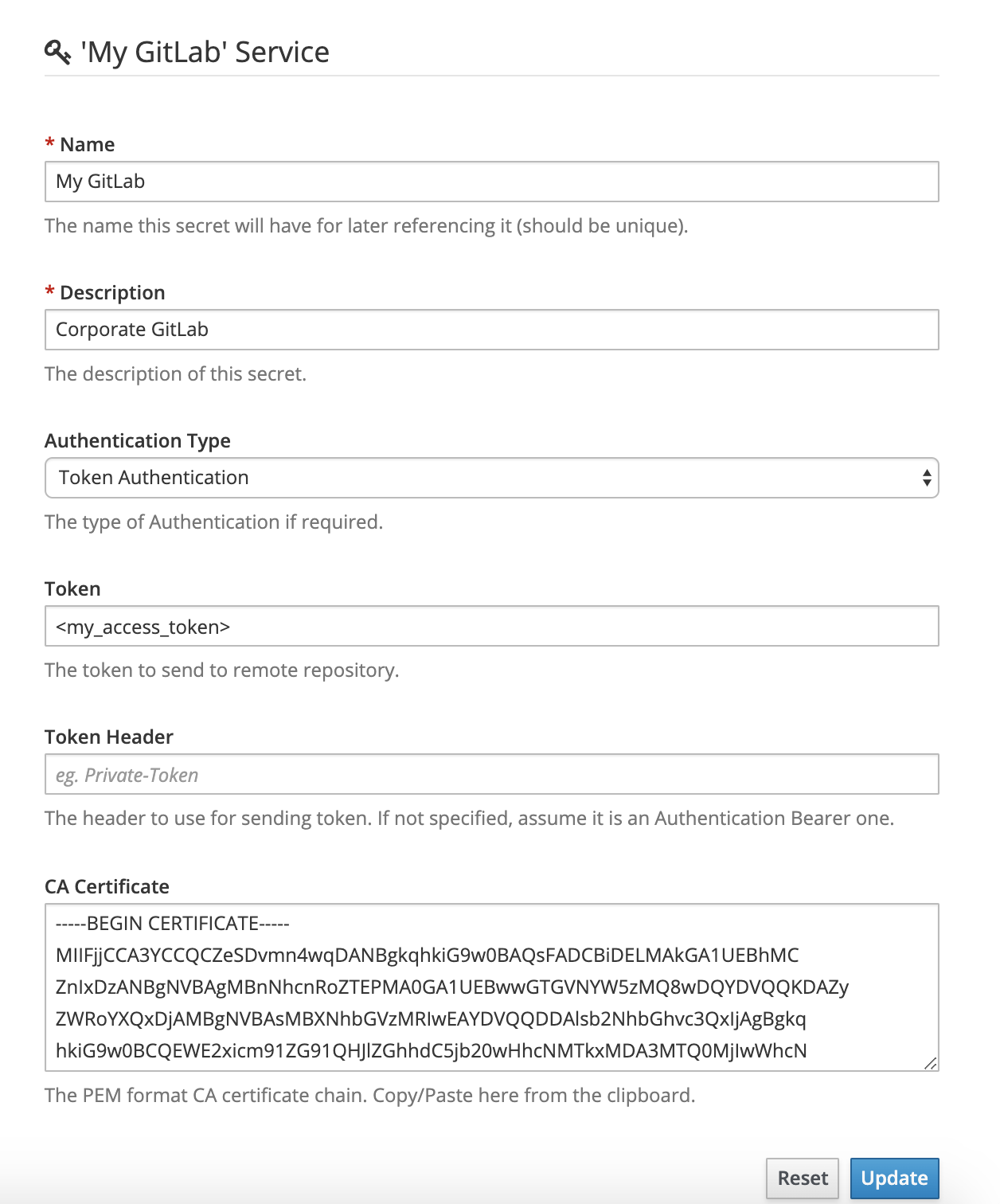
Authentication may be realized using different methods described below.
Authentication Type | Description |
|---|---|
None | No authentication is actually realized. In this case, the secret may only be useful to hold custom certificate to access private resource. |
Basic Authentication | An HTTP Basic authentication is attempted when connecting to remote resource. When selecting this method, form will just ask for a User and a Password. |
Token Authentication | An HTTP Bearer or custtom authentication is attempted with the prvided Token. If no Token-Header is specified, the standard Authentication: Bearer <provided token> is attempter. If a Token-Header is specified, token is added as the value of this specific header. |
The CA Certificate is just here to gather a custom certificate or certificate chain specified in PEM format
.
Using the form, you may create as much Secret as you need for different resources. Regular users of the Microcks instance will just have access to the name and the description of the secrets.
3. Adding a Secret to an Import Job
Now that you have created and managed your secrets, they can be reused when defining an Import Job. For doing that, just go and update a job: the second step of the wizard modal is dedicated to security concerns. You may now just add a reference to (thus a usage of) one of your secret.
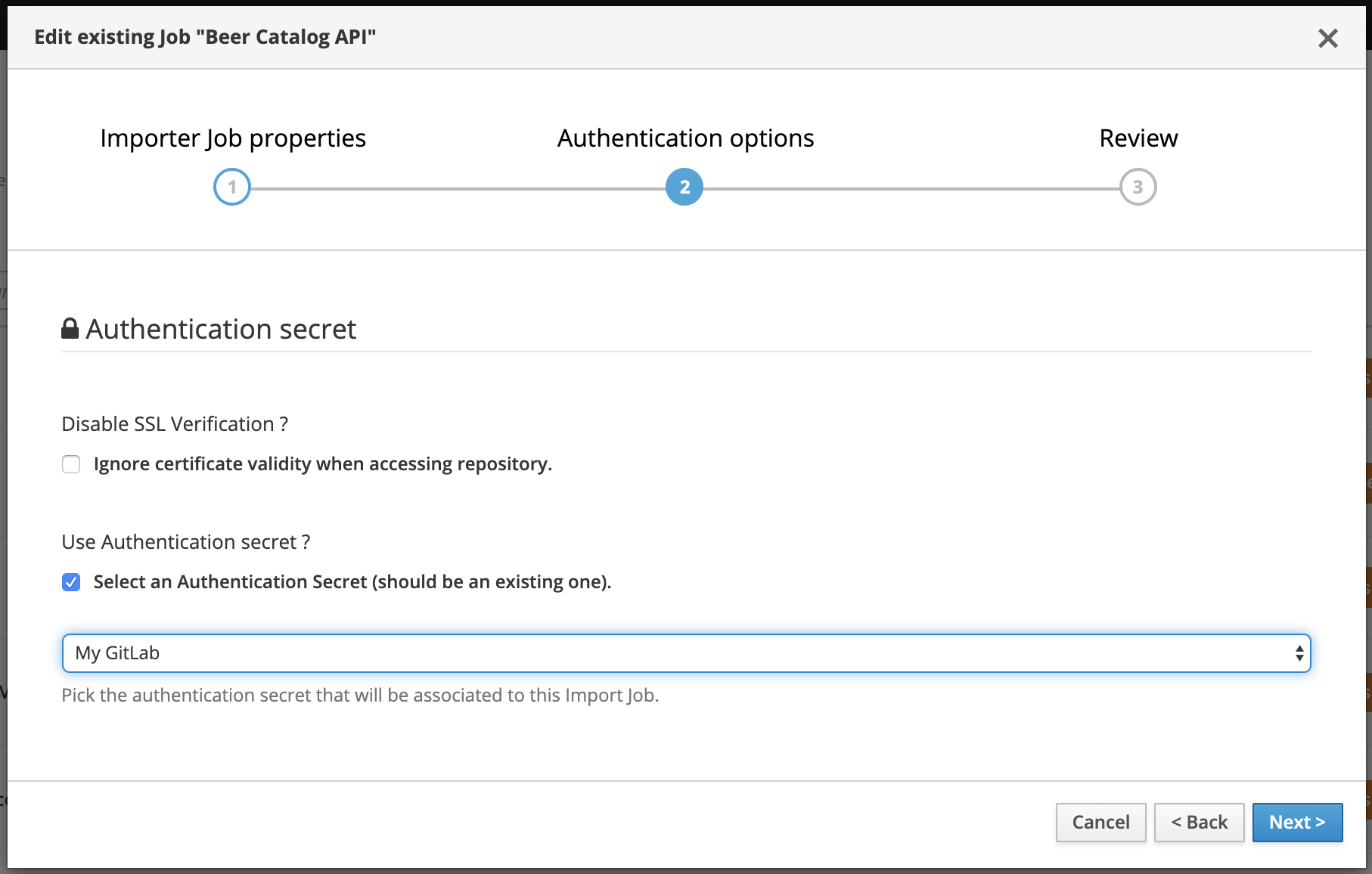
When Microcks will scheduled and execute this job to check update of artifact resource, it will simply used the referenced secret. Now your job is identified as using a secret with a balck lock 🔒 on the UI:

Each and every time the scheduled import job will be fired, it will reused the up-to-date informations of the secret to provide the correct token and certificates to the external resource.
Wrap-up
Following this guide, you have learned how Authentication Secrets allows you to hold credentials informations for accessing secured remote resources used by Microcks importers or tests. You should now be confident in the way Microcks access these protected resources, letting regular users just reference the Secret name.

Still Didn’t Find Your Answer?
Join our community and get the help you need. Engage with other members, ask questions, and share knowledge to resolve your queries and expand your understanding.
Join the community