Test Parameters
🗓️ Last updated on June 13, 2024 | 7 | Improve this pageIntroduction
From the page displaying basic information on your API or Service mocks , you have the ability to launch new tests against different endpoints that may be representing different environment into your development process. Hitting the NEW TEST… button, leads you to the following form where you will be able to specify a target URL for the test, as well as a Runner—a testing strategy for your new launch:
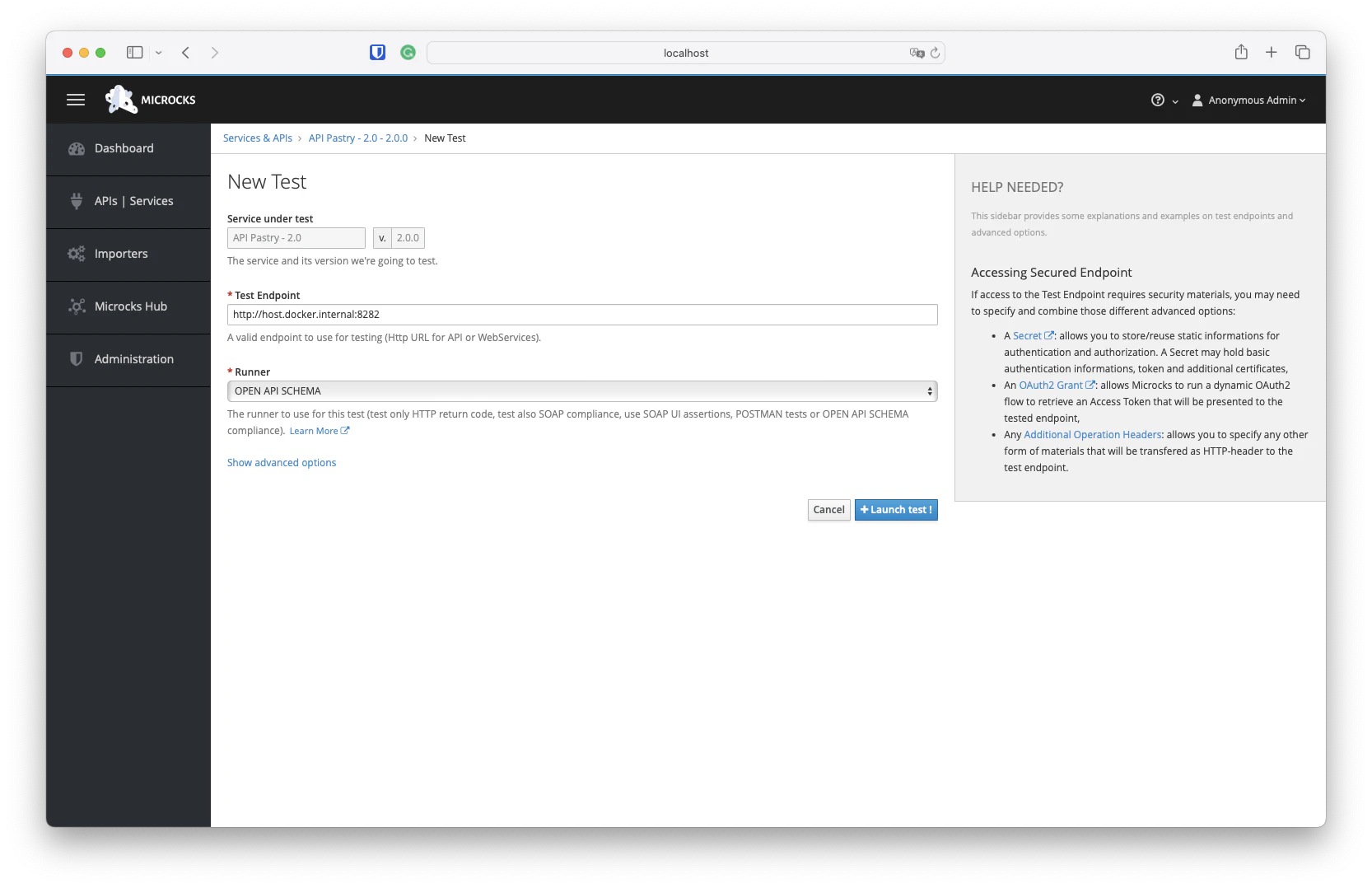
This reference documentation walks you through the different parameters available when launching a new test on Microcks. All the parameters mentioned below are available whether you’re launching a Test via the Web UI, via the API , via the CLI or any other libraries.
Service under test
Service under test is simply the reference of the API/Service specification we use as a reference for this test. This a couple of Service Name and Service Version. Depending on the Runner you choose, Microcks while reuse the information of an Artifact
attached to this Service name and version.
Test Endpoint
The Test Endpoint is simply a URI where a deployed component is providing an endpoint implementing your API specification. In the testing literature, this is usually defined as the URI of the System Under Test .
Depending on your API/Service type and the protocol binding you want to connect with (especially for event-based APIs), Test Endpoints mays have different specific syntax. Please jump to the Endpoints syntax section on this page to learn more.
Test Runner
Microcks offers different strategies for running tests on endpoints where our microservice being developed are deployed. We recommend having a read at our explanations on Conformance Testing . Such strategies are implemented as Test Runners. Here are the default Test Runners available within Microcks:
Test Runner | API & Service Types | Description |
|---|---|---|
HTTP | REST and SOAP | Simplest test runner that only checks that valid target endpoints are deployed and available - it means return a 20x or 404 Http status code when appropriated. This can be called a simple “smock test”. |
SOAP | SOAP | Extension of HTTP Runner that also checks that the response is syntactically valid regarding SOAP WebService contract. It realizes a validation of the response payload using XSD schemas associated to service. |
SOAP_UI | REST and SOAP | When the API artifact is defined using SoapUI : ensures that assertions put into SoapUI Test cases are checked valid. Report failures otherwise. |
POSTMAN | REST, SOAP and GRAPHQL | When the API artifact is defined using Postman : executes test scripts as specified within a Postman Collection. Report failures otherwise. |
OPEN_API_SCHEMA | REST | When the API artifact is defined using Open API : it executes example requests and check that results have the expected Http status and that payload is compliant with OpenAPI schema specified into OpenAPI specification. Report failures otherwise. |
ASYNC_API_SCHEMA | EVENT | When the API artifact is defined using Async API : it connects to specified broker endpoints, consume messages and check that payload is compliant with AsyncAPI schema specified into AsyncAPI specification. Report failures otherwise. |
GRPC_PROTOBUF | GRPC | When the API artifact is defined using gRPC/Protobuf : it executes example requests and check that results payload is compliant with Protocol Buffer schema specified into gRPC protobuffer file. Report failures otherwise. |
GRAPHQL_SCHEMA | GRAPHQL | When the API is of type GraphQL : it executes example requests and check that results payload is compliant with the GraphQL Schema of the API. Report failures otherwise. |
Operations
Depending on the Test your are running, you may want to filter the list of operations that will be actually tested. By default, all operations are included in the test but you can pick and choose the one you want.
💡 When running a Test on an Event-baed API using the
ASYNC_API_SCHEMAstrategy, you will have to choose one and only one operation at a time. This is because Async endpoints may be different for each and every operation so a Microcks tests can just include one Async operation.
Timeout
Depending on the type of Service or Tests you are running, the specification of a Timeout maybe mandatory. This is a numerical value expressed in milliseconds.
Secret
Depending on the Test Endpoint you are connecting to, you may need additional authentication information - like credentials or custom X509 Certificates. You may reuse an Authentication Secret that has been made available in the Microcks installation by your administrator.
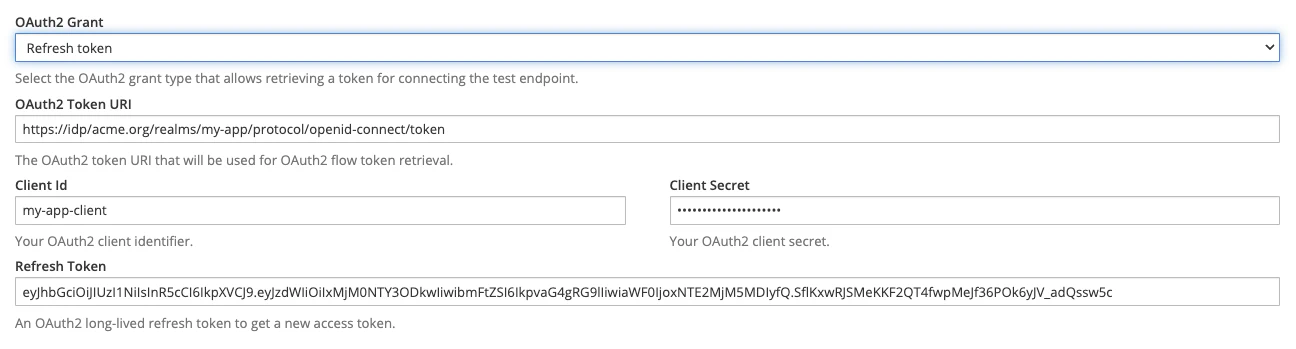
OAuth2
If the secured Test Endpoint cannot be accessed using a static Authentication Secret , Microcks is able to handle an OAuth2 / OpenID Connect authentication flow as the Tests prerequisites in order to retrieve an ephemeral bearer token.
The supported Oauth2 grant types are Client credentials, Refresh token and Password. For each of this authentication flow, you will have to provide additional information like:
- The OAuth2 Token URI: a URL that will be used for token retrieval,
- The Client Id: the OAuth2 client identifier,
- The Client Secret: the OAuth2 secret,
- The Scopes: the optional OAuth2 scopes you need (
openidis always included).
Additionally, you will have to provide a Refresh Token when using the Refresh token grant type 😉
Headers Override
This optional parameter allows you to add/override requests headers with global or operation specific ones. You have to use a comma-separated string for multiple values corresponding to the same header.
Endpoints syntax
HTTP based APIs
For HTTP based APIs (REST, SOAP, GraphQL or gRPC), this is a simple URL that should respect following pattern:
http[s]://{service.endpoint.url:port}[/{service.path}]
The /{service.path} may be optioanl if your target API is deployed on the root context.
Event based APIs
For Event based API through Async API testing, pattern is depending on the protocole binding you’d like to test.
Kafka
Kafka Test Endpoint have the following form with optional parameters placed just after a ? and separated using & character:
kafka://{kafka.broker.url:port}/{kafka.topic.name}[?param1=value1¶m2=value2]
| Optional Params | Description |
|---|---|
registryUrl | The URL of schema registry that is associated to the tested topic. This parameter is required when using and testing Avro encoded messages. |
registryUsername | The username used if access to the registry is secured. |
registryAuthCredSource | The source for authentication credentials if any. Valid values are just USER_INFO. |
As an example, you may have this kind of Test Endpoint value: kafka://mybroker.example.com:443/test-topic?registryUrl=https://schema-registry.example.com®istryUsername=fred:letmein®istryAuthCredSource=USER_INFO
MQTT
MQTT Test Endpoint have the following form with no optional parameters:
mqtt://{mqtt.broker.url:port}/{mqtt.topic.name}
AMQP
AMQP 0.9.1 Test Endpoint have the following form with optional parameters placed just after a ? and separated using & character:
amqp://{amqp.broker.url:port}/[{amqp.vhost}/]{amqp.destination.type}/{amqp.destination.name}[?param1=value1¶m2=value2]
amqp.destination.type is used to specify if we shoulf connect to either a queue (use the q value) or an exchange speciyfing its type: d dor direct, f for fanout, t for topic, h for headers. Then you have to specify either the queue or exchange name in amqp.detaintion.name.
Depending on the type of destination, you will need additional optional parameters as specified below:
| Optional Params | Description |
|---|---|
routingKey | Used to specify a routing key for direct or topic exchanges. If not specified the * wildcard is used. |
durable | Flag telling if exchange to connect to is durable or not. Default is false. |
h.{header} | A bunch of headers where name starts with h. in order to deal with headers exchange. The x-match property is set to anyto gather the most message as possible. |
As an example, you may have this kind of Test Endpoint values: amqp://rabbitmq.example.com:5672/h/my-exchange-headers?h.h1=h1&h.h2=h2 or amqp://rabbitmq.example.com:5672/my-vhost/t/my-exchange-topic?routingKey=foo
WebSocket
WebSocket Test Endpoint have the following form with no optional parameters
ws://{ws.endpoint.url:port}/{channel.name}
NATS
NATS Test Endpoint have the following form with no optional parameters:
nats://{nats.endpoint.url:port}/{queue-or-subject.name}
Google PubSub
Google PubSub Test Endpoint have the following form with no optional parameters:
googlepubsub://{google-platform-project.name}/{topic.name}
Amazon SQS
Amazon Simple Queue Service Test Endpoint have the following form with optional parameters placed just after a ? and separated using & character:
sqs://{aws.region}/{sqs.queue.name}[?param1=value1]
| Optional Params | Description |
|---|---|
overrideUrl | The AWS endpoint override URI used for API calls. Handy for using SQS via LocalStack |
Amazon SNS
Amazon Simple Notification Service Test Endpoint have the following form with optional parameters placed just after a ? and separated using & character:
sns://{aws.region}/{sns.topic.name}[?param1=value1]
| Optional Params | Description |
|---|---|
overrideUrl | The AWS endpoint override URI used for API calls. Handy for using SNS via LocalStack |

Still Didn’t Find Your Answer?
Join our community and get the help you need. Engage with other members, ask questions, and share knowledge to resolve your queries and expand your understanding.
Join the community